Food and beverage packaging molds play a crucial role in the production of packaging materials used in the food and beverage industry. Here's a general overview of how food and beverage packaging molds work:
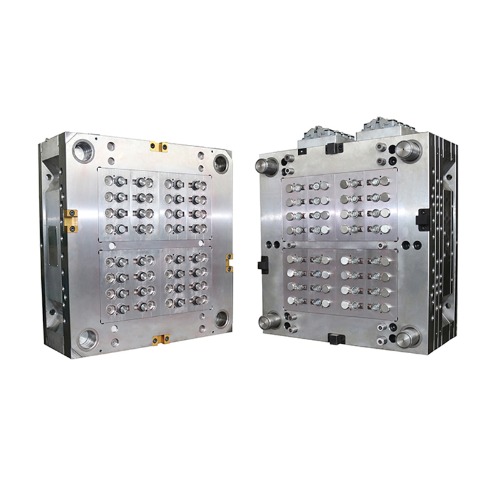
Mold Design: The first step is to design the mold based on the specific requirements of the packaging product. This includes determining the shape, size, and features of the packaging container or component. Mold designers consider factors such as product dimensions, material flow, wall thickness, and ejection mechanisms during this stage.
Mold Manufacturing: Once the mold design is finalized, the mold manufacturing process begins. The mold is typically made from materials such as steel or aluminum. Complex molds may consist of multiple parts that fit together to form the desired shape of the packaging product.
Injection Molding: Injection molding is the primary method used to produce food and beverage packaging materials. The mold is mounted onto an injection molding machine, which consists of a heating and injection system. Plastic resin pellets, often made of materials such as polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), or polyethylene terephthalate (PET), are fed into a hopper and melted into a molten state.
Injection and Cooling: The molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity under high pressure through a nozzle and runner system. The plastic fills the cavities and takes the shape of the mold. Cooling channels within the mold help dissipate heat, solidifying the plastic into the desired shape.
Ejection: Once the plastic has solidified, the mold opens, and an ejection system pushes or extracts the newly formed packaging product out of the mold. This can involve ejector pins or other mechanisms to facilitate the release of the product from the mold.
Finishing: Depending on the specific requirements, additional finishing steps may be performed on the packaging product. This can include trimming excess material, removing flash (excess plastic), adding logos or labels, or applying surface treatments like embossing or texturing.
Quality Control: Throughout the production process, quality control measures are implemented to ensure the molded packaging products meet the required standards. This can involve visual inspections, dimensional checks, and testing for factors such as wall thickness, strength, and product integrity.
Food and beverage packaging molds enable the efficient and precise production of various packaging components, such as bottles, caps, containers, trays, and lids. The molds are designed to provide consistent and high-quality packaging products that meet the specific requirements of the food and beverage industry in terms of safety, hygiene, functionality, and aesthetics.




 English
English Español
Español










