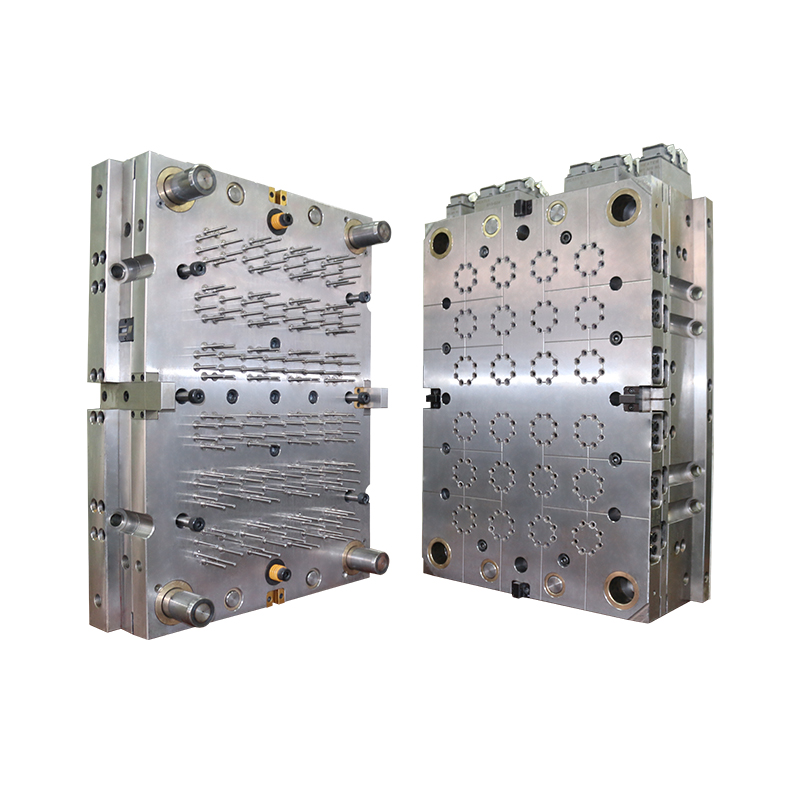
The desired surface finish significantly influences the selection of materials for Medical Parts Injection Moulds, particularly in the context of biocompatibility and sterilization compatibility. Here's a detailed breakdown of how the desired surface finish considerations impact material selection:
Biocompatibility Requirements:
The surface finish directly affects the interaction between the medical device components and the human body. Biocompatibility is a critical consideration, ensuring that the materials and surface finishes do not elicit adverse reactions when in contact with biological tissues or fluids.
Materials chosen for injection molds must have inherent biocompatible properties and compatibility with the intended medical application. The surface finish should enhance biocompatibility by creating a smooth, non-reactive, and easily cleanable surface.
Smooth and Non-Porous Surfaces:
A smooth and non-porous surface finish is essential for medical components to minimize the risk of microbial adhesion and facilitate easy cleaning and sterilization. Surface irregularities or pores can harbor contaminants, compromising the cleanliness of the medical device.
Materials with inherently smooth surfaces and the ability to retain smoothness even after molding processes are preferred. Non-porous materials are chosen to prevent the accumulation of contaminants and facilitate effective sterilization.
Ease of Cleaning and Sterilization:
The surface finish directly influences the ease of cleaning and sterilization processes. A smooth surface allows for thorough cleaning, while certain finishes may resist or impede the effectiveness of sterilization methods.
Materials selected should allow for the achievement and maintenance of a smooth surface finish. Additionally, the material must be compatible with common sterilization methods, such as autoclaving or ethylene oxide gas, without compromising its structural integrity or biocompatibility.

Resistance to Chemicals and Disinfectants:
Medical components may be exposed to various chemicals and disinfectants during cleaning and sterilization. The surface finish must resist chemical degradation to maintain its integrity and biocompatibility.
Materials chosen should have inherent resistance to common medical-grade disinfectants and cleaning agents. Compatibility with these substances is crucial to ensure the material remains stable and does not introduce harmful substances to the medical device.
Regulatory Compliance:
Regulatory standards for medical devices often include specifications for surface characteristics. The surface finish must align with these standards to ensure compliance and market approval.
Materials selected for injection molds must meet regulatory requirements for biocompatibility and surface characteristics. The choice of materials should facilitate the achievement of the desired surface finish in line with regulatory expectations.
Material Compatibility with Molding Processes:
Different materials respond differently to molding processes, and the selected material must allow for the achievement of the desired surface finish without introducing defects or inconsistencies.
Materials compatible with injection molding processes and capable of producing smooth surfaces without the need for extensive post-processing treatments are preferred. This ensures efficiency in manufacturing while meeting surface finish requirements.


 English
English Español
Español










