Performing functional testing on medical parts produced by an Medical Parts Injection Mould is crucial to ensure that the products meet the required standards and functional specifications. Here's a general overview of the process:
1. Define Functional Requirements:
Clearly define the functional requirements and specifications of the medical part. This includes understanding its intended use, performance criteria, and any regulatory standards it must adhere to.
2. Select Testing Methods:
Choose appropriate testing methods based on the specific functional requirements of the medical part. Common methods include:
Flow and Pressure Testing: For fluidic components such as valves, connectors, and tubing, perform flow and pressure tests to ensure that the component functions as intended under various flow rates and pressures.
Leak Testing: Conduct leak tests using methods like pressure decay testing, vacuum decay testing, or bubble emission testing to check for any fluid or gas leaks.
Functional Mockups: Create functional mockups or assemblies that mimic the intended use of the medical part. For example, assemble a complete medical device and assess how the part interacts within the system.
Durability Testing: Subject the part to repeated cycles or stress tests to evaluate its durability and longevity.
Electrical and Electronic Testing: If the part includes electrical or electronic components, perform electrical tests, such as continuity testing, voltage measurements, or resistance checks.
Dimensional Checks: Ensure that critical dimensions of the part, which affect its function, are within tolerance using appropriate measurement tools.
3. Test Setup:
Set up a controlled testing environment that closely simulates the conditions the medical part will encounter during its intended use. This may include controlling temperature, pressure, humidity, or other environmental factors.
4. Instrumentation and Data Collection:
Use suitable instrumentation to collect data during testing. Data loggers, pressure transducers, sensors, and cameras can be employed to record relevant parameters.
5. Testing Procedures:
Follow standardized testing procedures, if available, or develop custom test protocols that align with the specific functional requirements and standards of the medical part.
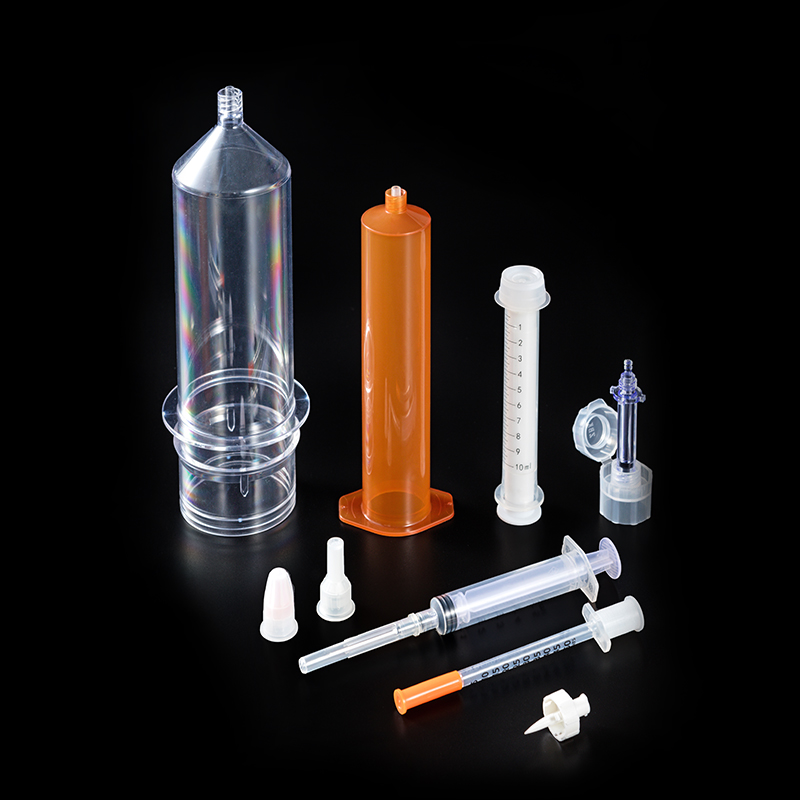

6. Execute Tests:
Perform the functional tests as per the defined procedures. Monitor and record data during testing to assess the performance of the medical part.
7. Data Analysis:
Analyze the collected data to determine whether the medical part meets the functional requirements and standards. Look for any deviations, anomalies, or failures.
8. Documentation and Reporting:
Maintain detailed records of the testing process, including setup, procedures, data collected, and results. If the medical part passes all tests, document the compliance. If failures or issues are identified, document them thoroughly.
9. Retesting and Iteration:
If the part does not meet the functional requirements or standards, investigate the root cause of the issues, make necessary design or manufacturing adjustments, and retest until compliance is achieved.
10. Regulatory Considerations:
Ensure that the functional testing process aligns with regulatory requirements, such as those outlined by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or other relevant regulatory bodies in your region.
Functional testing is a critical step in the production of medical parts, as it ensures that the components will perform reliably and safely in their intended applications, ultimately contributing to patient safety and the effectiveness of medical devices.


 English
English Español
Español










